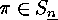 is the list notation,
where we put the list
of their values in square brackets:
is the list notation,
where we put the list
of their values in square brackets:
Another way of
describing permutations 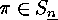 is the list notation,
where we put the list
of their values in square brackets:
is the list notation,
where we put the list
of their values in square brackets:
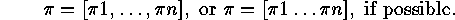
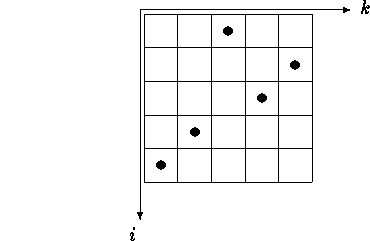
In order to visualize permutations we can use a board consisting of boxes in the
second quadrant, where we put a black button  into the box with the pair of coordinates
into the box with the pair of coordinates
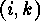 if and only
if and only 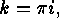 obtaining the Rothe diagram
obtaining the Rothe diagram
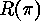 of
of 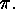 This diagram was introduced by
H. A. Rothe already in 1800. For example
This diagram was introduced by
H. A. Rothe already in 1800. For example
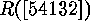 is equal to
is equal to
The list notation gives rise to the Lehmer code
which we are going to describe next. In order to do this we consider
the set 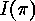 of inversions of
of inversions of 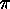 :
:
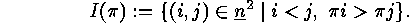
An easy check (exercise ![]() ) shows that the following holds:
) shows that the following holds:
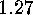 .
.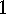 Lemma
If we represent the inversion
Lemma
If we represent the inversion 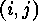 of
of 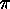 by a white button
by a white button
 at
at 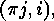 then we fill exactly the boxes of the Rothe diagram
of
then we fill exactly the boxes of the Rothe diagram
of 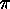 where the black button of the row is in a column to the right and where
the black button of the column is lower down.
where the black button of the row is in a column to the right and where
the black button of the column is lower down.
The resulting diagram 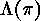 is called the Lehmer diagram
of
is called the Lehmer diagram
of 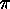 . For example, the superposition of the Rothe diagram and the Lehmer
diagram of
. For example, the superposition of the Rothe diagram and the Lehmer
diagram of 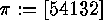 is
is
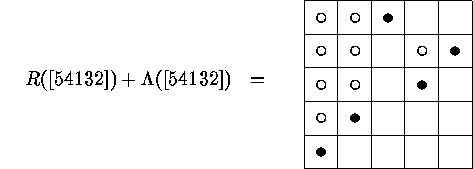
There is a program, which calculates the number of inversions of a given permutation.
Exercises