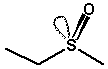Chirality: Elements of chirality
|
Center of chirality, chiral center: "an atom bearing a set of substituents in a spatial arrangement that is not superposable to its mirror image arrangement." (Quote from Hellwich, translated by C.R.)
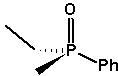
Examples (apart from the usual asymmetric C atom):
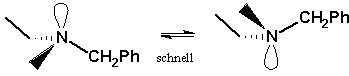
The three substituents and the lone pair at an amine N atom are arranged tetrahedrically. However, by fast inversion of the N atom the enantiomers interconvert, such that an amine N atom is not normally considered a center of chirality. |